Definify.com
Webster 1913 Edition
Comminute
Com′mi-nute
,Verb.
T.
[
imp. & p. p.
Comminuted
; p. pr. & vb. n.
Comminuting
.] To reduce to minute particles, or to a fine powder; to pulverize; to triturate; to grind;
as, to
. comminute
chalk or bones; to comminute
food with the teethPennant.
Comminuted fracture
. See under
Fracture
.Webster 1828 Edition
Comminute
COMMINUTE
,Verb.
T.
Definition 2025
comminute
comminute
English
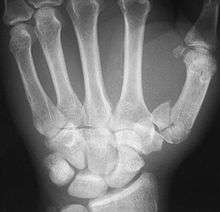
An x-ray showing a comminuted metacarpal bone fracture

Verb
comminute (third-person singular simple present comminutes, present participle comminuting, simple past and past participle comminuted)
- To pulverize; to smash.
- 1991, David Segal, Chemical Synthesis of Advanced Ceramic Materials, page 20,
- High temperatures required for reaction between components can result in loss of volatile oxides, while milling may not comminute powders sufficiently for complete reaction to occur on calcination.
- 2000, Denise M. Smith, Chapter Eleven: Functional properties of muscle proteins in processed poultry products, Alan R. Sams (editor), Poultry Meat Processing, 2nd Edition, page 186,
- Collagen may cause shrinkage of comminuted meat products, especially when cooked to high temperatures, or interfere in binding between meat pieces in formed products.
- 2011, William L. Cooper, Communication of Stresses by Chains of Grains in High-Speed Particulate Media Impacts, Tom Proulx (editor), Dynamic Behavior of Materials, Volume 1: Proceedings of the 2011 Annual Conference on Experimental and Applied Mathematics, page 100,
- High pressure directly ahead of and beside the projectile nose comminute and fracture the sand media, forming a rigid, conical false nose on the front of the projectile.
- 2012, James G. Brennan, 11: Mixing, Emulsification, and Size Reduction, James G. Brennan, Alistair S. Grandison (editors), Food Processing Handbook, 2nd Edition, unnumbered page,
- Such mills are used for comminuting relatively soft materials, such as fruit and vegetable matter.
- 1991, David Segal, Chemical Synthesis of Advanced Ceramic Materials, page 20,
- (medicine) To cause fragmentation (of bone).
- 2008, Erin H. Kimmerle, Jose Pablo Baraybar, Skeletal Trauma: Identification of Injuries Resulting from Human Rights Abuse and Armed Conflict, page 410,
- For example, comminuting fractures on ribs 4–8 along the rib angle most likely are associated to shots through the scapula, whereas injuries through or near to the costochondral articulation of the first rib could also be associated to wounds of the sternum or clavicle.
- 2011, S. John Ham, Matthijs R. Krijnen, Rudolf W. Poolman, 48: Forearm Fractures, Including Galeazzi Fractures, Mohit Bhandari (editor), Evidence-based Orthopedics, page 419,
- In the past, there have been controversies over the use of bone graft in comminuted fractures of the forearm.
- 2011, Sean D. Early, Vernon T. Tolo, 9: Pediatric Elbow Fractures, Raffy Mirzayan, John M. Itamura (editors), Shoulder and Elbow Trauma, page 127,
- When using reduction forceps, care must be taken to prevent comminuting the medial epicondylar fragment.
- 2008, Erin H. Kimmerle, Jose Pablo Baraybar, Skeletal Trauma: Identification of Injuries Resulting from Human Rights Abuse and Armed Conflict, page 410,
- To break into smaller portions.
Noun
comminute (plural comminutes)
- Pulverized material.
- The drink contains lemon comminute.
- 1975, Hallie B. North, Commercial Food Patents, U.S. 1975, page 166,
- A method of making a restructured meat product in the form of small pieces from a comminute of raw meat, comprising: […] .
- 1994, A. Varnam, J.M. Sutherland, Beverages: Technology, Chemistry and Microbiology, page 81,
- Fruit flavour may be added as juice, as a comminute (in the case of citrus fruit) or as an essence. […] Citrus comminutes are made from the whole fruit, in contrast to juice which is expressed from the pericarp.
- 2008, P. R. Ashurst, 6: Non-carbonated beverages, Philip R. Ashurst (editor), Chemistry and Technology of Soft Drinks and Fruit Juices, page 132,
- The typical concentrated juices and comminutes used by the industry for manufacturing dilutable drinks are shown in Table 6.3.