Definify.com
Definition 2026
無
無
Translingual
| Stroke order (cursive) | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||

Han character
無 (radical 86 火+8, 12 strokes, cangjie input 人廿火 (OTF), four-corner 80331, composition ⿱⿳𠂉卌一灬)
Derived characters
References
- KangXi: page 673, character 26
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 19113
- Dae Jaweon: page 1081, character 24
- Hanyu Da Zidian: volume 3, page 2211, character 15
- Unihan data for U+7121
Chinese
| trad. | 無 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. | 无 | |
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 無
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Large seal script | Small seal script |
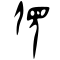 |
 |
 |
 |
| Characters in the same phonetic series (無) (Zhengzhang, 2003) | |
|---|---|
| Old Chinese | |
| 墲 | *m̥ʰaː, *maː, *ma |
| 橅 | *maː |
| 膴 | *hmaː, *ma, *maʔ |
| 幠 | *hmaː |
| 鄦 | *hmaʔ |
| 撫 | *m̥ʰaʔ |
| 無 | *ma |
| 瞴 | *ma, *maʔ |
| 蕪 | *ma |
| 璑 | *ma |
| 鷡 | *ma |
| 譕 | *ma |
| 憮 | *ma, *maʔ |
| 舞 | *maʔ |
| 廡 | *maʔ |
| 嫵 | *maʔ |
| 甒 | *maʔ |
| 潕 | *maʔ |
| 儛 | *maʔ |
Simplified from 舞 (舛 → 灬) – removal of 舛 (character used for sound). (Compare 可 from 奇.)
In the source character 舞 (OC *maʔ, “dance”), top component graphically originally a figure with outstretched arms holding two animal hides: 革 + 大 + 革.
Etymology 1
Core Sino–Tibetan. From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *ma (“no, not”); cognate with Tibetan མ (ma, “not”) and Burmese မ (ma., “not”).
Cognate with:
- 微 (OC *mɯl, “not, no”)
- 毋 (OC *ma, “do not”)
- 勿 (OC *mɯd, “not, don't”)
- 未 (OC *mɯds, “not yet, haven't”)
- 靡 (OC *mralʔ, “not, no”)
- 亡 (OC *maŋ, “not have; to flee, to disappear, to die”)
- 沒 (OC *mɯːd, “to end, to disappear, to drown”)
- 莫 (OC *maːɡ, “none, nobody, nothing; do not; can not”)
Attested profusely in Classical Chinese, this word is the prototypical negation particle in the *m- series of Chinese negatives. In the oracle bone script, however, 無 is not frequently used, and its homophone (or near-homophone) 毋 (OC *ma) is used instead.
See 不 (OC *pɯ, *pɯʔ, *pɯ', “not”) for more on negative particles in Old Chinese.
Pronunciation
- Mandarin
- Cantonese (Jyutping): mou4
- Hakka (Sixian, PFS): vù / mò
- Min Dong (BUC): mò̤ / ù
- Min Nan
- Wu (Wiktionary): hhmm (T3); vu (T3)
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄨˊ
- Wade-Giles: wu2
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: wu
- IPA (key): /u³⁵/
-

- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Jyutping: mou4
- Yale: mòuh
- Cantonese Pinyin: mou4
- IPA (key): /mou̯²¹/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: vù / mò
- Hakka Romanization System: vuˇ / moˇ
- Hagfa Pinyim: vu2 / mo2
- IPA: /vu¹¹/, /mo¹¹/
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Min Dong
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: mò̤ / ù
- IPA (key): /mo⁵³/, /u⁵³/
- Note: mò̤ - colloquial; ù - literary.
- (Fuzhou)
- Min Nan
- (Hokkien)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: bô / bû
- Tâi-lô: bô / bû
- Phofsit Daibuun: booi, buu
- IPA (Xiamen): /bɤ²⁴/, /bu²⁴/
- IPA (Quanzhou): /bɤ²⁴/, /bu²⁴/
- IPA (Zhangzhou): /bɤ¹³/, /bu¹³/
- IPA (Taipei): /bo²⁴/, /bu²⁴/
- IPA (Kaohsiung): /bɤ²³/, /bu²³/
-

- Note: bô - colloquial; bû - literary.
- (Teochew)
- Peng'im: bho5 / bhu5
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī-like: bô / bû
- IPA (key): /bo⁵⁵/, /bu⁵⁵/
- Note: bho5 - colloquial; bhu5 - literary.
- (Hokkien)
- Wu
- (Shanghainese)
- Wiktionary: hhmm (T3); vu (T3)
- IPA (key): /ɦm̩²³/, /v̻v̩ʷ²³/
- Note: 3hhmm - colloquial; 3vu - literary.
- (Shanghainese)
| Rime | |
|---|---|
| Character | 無 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| Initial (聲) | 明 (4) |
| Final (韻) | 虞 (24) |
| Tone (調) | Level (Ø) |
| Openness (開合) | Closed |
| Division (等) | III |
| Fanqie | 武夫切 |
| Reconstructions | |
| Zhengzhang Shangfang |
/mɨo/ |
| Pan Wuyun |
/mio/ |
| Shao Rongfen |
/mio/ |
| Edwin Pulleyblank |
/muə̆/ |
| Li Rong |
/mio/ |
| Wang Li |
/mĭu/ |
| Bernard Karlgren |
/mi̯u/ |
| Expected Mandarin Reflex |
wú |
| Baxter-Sagart system 1.1 (2014) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Character | 無 | 無 | 無 |
| Reading # | 1/3 | 2/3 | 3/3 |
| Modern Beijing (Pinyin) |
wú | wú | wú |
| Middle Chinese |
‹ mju › | ‹ mju › | ‹ mju › |
| Old Chinese |
/*ma/ | /*ma/ | /*mo/ |
| English | not have | volitional prefix | don’t |
Notes for Old Chinese notations in the Baxter-Sagart system: * Parentheses "()" indicate uncertain presence; | |||
| Zhengzhang system (2003) | |
|---|---|
| Character | 無 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| No. | 13117 |
| Phonetic component |
無 |
| Rime group |
魚 |
| Rime subdivision |
0 |
| Corresponding MC rime |
無 |
| Old Chinese |
/*ma/ |
Definitions
無
- (literary, Hakka or Min) to not have something; there is not ...
- (literary, Min) Negation particle preceding verbs and adjectives. not
- (literary, Min) have not
- (literary, Hakka or Min) Interrogative particle.
- (Hakka, Min) if not; otherwise (placed at the start of a sentence)
- †regardless of, no matter whether
- †nothing, nil
- 從無到有 / 从无到有 ― cóng wú dào yǒu ― start from nothing, from scratch
- †Alternative form of 毋 (wú, “do not”).
- without, -less, un-
Synonyms
| Dialectal synonyms of 沒有 (“to not have (+ noun)”) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variety | Location | Words |
| Classical Chinese | 無 | |
| Formal (Written Standard Chinese) | 沒有 | |
| Mandarin | Beijing | 沒有、沒 |
| Taiwan | 沒有、沒 | |
| Jinan | 沒有、沒 | |
| Xi'an | 沒有 | |
| Wuhan | 冇得 | |
| Chengdu | 沒得 | |
| Yangzhou | 不得、沒得 | |
| Hefei | 沒 | |
| Cantonese | Guangzhou | 冇、冇有 |
| Hong Kong | 冇 | |
| Taishan | 冇 | |
| Gan | Nanchang | 冒有 |
| Hakka | Meixian | 無 |
| Miaoli (N. Sixian) | 無 | |
| Liudui (S. Sixian) | 無 | |
| Hsinchu (Hailu) | 無 | |
| Dongshi (Dabu) | 無 | |
| Zhuolan (Raoping) | 無 | |
| Yunlin (Zhao'an) | 無 | |
| Jin | Taiyuan | 沒、沒啦 |
| Min Dong | Fuzhou | 無 |
| Min Nan | Quanzhou | 無 |
| Xiamen | 無 | |
| Zhangzhou | 無 | |
| Taipei | 無 | |
| Kaohsiung | 無 | |
| Tainan | 無 | |
| Taichung | 無 | |
| Yilan | 無 | |
| Lukang | 無 | |
| Sanxia | 無 | |
| Kinmen | 無 | |
| Magong | 無 | |
| Hsinchu | 無 | |
| Malaysia | 無 | |
| Singapore | 無 | |
| Philippine | 無 | |
| Chaozhou | 無 | |
| Shantou | 無 | |
| Thailand | 無 | |
| Wu | Shanghai | 嘸沒 |
| Suzhou | 嘸不 | |
| Wenzhou | 冇 | |
| Xiang | Changsha | 冇得、冇 |
| Shuangfeng | 冇得 | |
Compounds
|
|
|
Etymology 2
Pronunciation
- Mandarin
- Cantonese (Jyutping): mo4
- Hakka (Sixian, PFS): mò
- Min Dong (BUC): mŏ
- Wu (Wiktionary): mo (T3)
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄇㄛˊ
- Wade-Giles: mo2
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: mo
- IPA (key): /mu̯ɔ³⁵/
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Jyutping: mo4
- Yale: mòh
- Cantonese Pinyin: mo4
- IPA (key): /mɔː²¹/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: mò
- Hakka Romanization System: moˇ
- Hagfa Pinyim: mo2
- IPA: /mo¹¹/
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Min Dong
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: mŏ
- IPA (key): /mu⁵⁵/
- (Fuzhou)
- Wu
- (Shanghainese)
- Wiktionary: mo (T3)
- IPA (key): /mo²³/
- (Shanghainese)
Definitions
無
- Only used in 南無/南无.
Compounds
Japanese
Kanji
Readings
Compounds
|
|
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 無 |
|
む Grade: 4 |
| on'yomi |
Noun
- nothing, nothingness
- (Buddhism): The null set: neither yes nor no (in response to a koan or other question that mistakenly assumes an affirmative or negative answer).
