Definify.com
Definition 2026
機
機
Translingual
| Shinjitai | 机/機 |
|---|---|
| Simplified | 机 |
| Traditional | 机/機 |
Han character
機 (radical 75 木+12, 16 strokes, cangjie input 木女戈戈 (DVII), four-corner 42953, composition ⿰木幾)
Descendants
References
- KangXi: page 554, character 8
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 15561
- Dae Jaweon: page 942, character 20
- Hanyu Da Zidian: volume 2, page 1298, character 4
- Unihan data for U+6A5F
Chinese
| trad. | 機 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. | 机 | |
Glyph origin
| Characters in the same phonetic series (幾) (Zhengzhang, 2003) | |
|---|---|
| Old Chinese | |
| 機 | *kɯl |
| 譏 | *kɯl |
| 嘰 | *kɯl |
| 磯 | *kɯl |
| 鞿 | *kɯl |
| 饑 | *kɯl |
| 禨 | *kɯl, *kɯls |
| 幾 | *kɯl, *kɯlʔ, *ɡɯl, *ɡɯls |
| 鐖 | *kɯl |
| 僟 | *kɯl |
| 璣 | *kɯl |
| 蟣 | *kɯlʔ, *ɡɯl |
| 穖 | *kɯlʔ |
| 畿 | *ɡɯl |
Phono-semantic compound (形聲, OC *kɯl) : semantic 木 + phonetic 幾 (OC *kɯl, *kɯlʔ, *ɡɯl, *ɡɯls).
Pronunciation
- Mandarin
- Cantonese (Jyutping): gei1
- Hakka (Sixian, PFS): kî
- Min Dong (BUC): gĭ
- Min Nan (POJ): ki / kui
- Wu (Wiktionary): ji (T1)
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄐㄧ
- Wade-Giles: chih1
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: ji
- IPA (key): /t͡ɕi⁵⁵/
-

- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Jyutping: gei1
- Yale: gēi
- Cantonese Pinyin: gei1
- IPA (key): /kei̯⁵⁵/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: kî
- Hakka Romanization System: gi´
- Hagfa Pinyim: gi1
- IPA: /ki²⁴/
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Min Dong
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: gĭ
- IPA (key): /ki⁵⁵/
- (Fuzhou)
- Min Nan
- Wu
- (Shanghainese)
- Wiktionary: ji (T1)
- IPA (key): /t͡ɕi⁵³/
- (Shanghainese)
| Rime | |
|---|---|
| Character | 機 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| Initial (聲) | 見 (28) |
| Final (韻) | 微 (20) |
| Tone (調) | Level (Ø) |
| Openness (開合) | Open |
| Division (等) | III |
| Fanqie | 居依切 |
| Reconstructions | |
| Zhengzhang Shangfang |
/kɨi/ |
| Pan Wuyun |
/kɨi/ |
| Shao Rongfen |
/kiəi/ |
| Edwin Pulleyblank |
/kɨj/ |
| Li Rong |
/kiəi/ |
| Wang Li |
/kĭəi/ |
| Bernard Karlgren |
/ke̯i/ |
| Expected Mandarin Reflex |
jī |
| Baxter-Sagart system 1.1 (2014) | |
|---|---|
| Character | 機 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| Modern Beijing (Pinyin) |
jī |
| Middle Chinese |
‹ kjɨj › |
| Old Chinese |
/*kəj/ |
| English | mechanism |
Notes for Old Chinese notations in the Baxter-Sagart system: * Parentheses "()" indicate uncertain presence; | |
| Zhengzhang system (2003) | |
|---|---|
| Character | 機 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| No. | 5788 |
| Phonetic component |
幾 |
| Rime group |
微 |
| Rime subdivision |
1 |
| Corresponding MC rime |
機 |
| Old Chinese |
/*kɯl/ |
Definitions
機
- weaving machine; spinning machine
- machine; apparatus; device
- Short for 飛機 (“aircraft”).
- mechanism; process
- cause; reason
- secret; confidential (affair)
- opportunity; chance; crucial point
- plan; idea
- flexible; quick-witted
Compounds
|
|
|
Japanese
Kanji
Readings
Compounds
Usage notes
Often used interchangeably in compounds with 器 (ki) to indicate “machine”, with the distinction that 機 implies a larger machine, such as an airplane, while 器 implies a smaller device, possibly hand-held. Compare 飛行機 (hikōki, “airplane”) with 食器 (shokki, “tableware”).
Alternative forms
機 has many ryakuji (handwritten abbreviations), as it is a common character with many strokes (16):
-
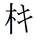 A phono-semantic simplification from on'yomi of “ki” (katakana キ): 木 + キ (semantic plus simplified phonetic) – compare
A phono-semantic simplification from on'yomi of “ki” (katakana キ): 木 + キ (semantic plus simplified phonetic) – compare  for 議 and
for 議 and  for 魔/摩.
for 魔/摩. -
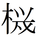 Graphical simplification.
Graphical simplification. -
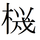 Graphical simplification.
Graphical simplification. -
 Graphical simplification.
Graphical simplification.
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 機 |
|
き Grade: 4 |
| on'yomi |
From Middle Chinese 機 (kjɨj, “mechanism”). Compare modern Min Nan reading ki.
Pronunciation
Noun
- a machine, a device; a contraption
- a loom
- an opportunity, a chance to do something; the right time or moment
- something of great importance: the linchpin of the matter
- resourcefulness
- (Buddhism) the moment of being moved into action by the teachings of the Buddha: see 機根 (kikon)
- by extension, the workings of the heart or mind in general
- in Noh theater, the breath of the mind
- short for 飛行機 (hikōki): an airplane, an aircraft
- short for 機関銃 (kikanjū): a machine gun
Idioms
|
Etymology 2
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 機 |
|
こぶち Grade: 4 |
| kun'yomi |
Alteration from こうべうち (kōbeuchi),[3] itself a compound of 首 (kōbe, “head”) + 打ち (uchi, “striking, hitting”).[3][1]
Pronunciation
Alternative forms
- 首打
Noun
機 (hiragana こぶち, romaji kobuchi)
Etymology 3
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 機 |
|
はた Grade: 4 |
| kun'yomi |
From onomatopoeic はた (hata), possibly for the sound of the shuttle running back and forth, or for the sound of a woven cloth moving in the wind, compare 旗 (hata, “a flag”).
Pronunciation
Noun
Etymology 4
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 機 |
|
わかつり Grade: 4 |
| kun'yomi |
The 連用形 (ren'yōkei, “continuative or stem form”) of verb 機る (wakatsuru, “to manipulate something”),[3] itself an alteration of 誘る (okotsuru, “to manipulate or con someone”),[3] a compound of 痴 (oko, “a fool”) + 釣る (tsuru, “to fish, to draw out”).[3]
Pronunciation
Noun
機 (hiragana わかつり, romaji wakatsuri)
- to manipulate (as in a device)
- to manipulate (as in a person): to deceive, to take in someone
- to get on someone's right side; to humor someone; to make an effort to please someone
References
- 1 2 3 4 2006, 大辞林 (Daijirin), Third Edition (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Sanseidō, ISBN 4-385-13905-9
- 1 2 1998, NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 (NHK Japanese Pronunciation Accent Dictionary) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: NHK, ISBN 978-4-14-011112-3
- 1 2 3 4 5 1988, 国語大辞典(新装版) (Kokugo Dai Jiten, Revised Edition) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan
Korean
Hanja
機 • (gi) (hangeul 기, McCune-Reischauer ki, Yale ki)
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.