Definify.com
Definition 2026
父
父
Translingual
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Han character
父 (radical 88 父+0, 4 strokes, cangjie input 金大 (CK), four-corner 80400)
- Kangxi radical #88, ⽗ (“father”).
See also
References
- KangXi: page 690, character 1
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 19721
- Dae Jaweon: page 1103, character 1
- Hanyu Da Zidian: volume 3, page 2039, character 1
- Unihan data for U+7236
Chinese
|
simp. and trad. |
父 | |
|---|---|---|
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 父
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Bamboo and silk script | Large seal script | Small seal script |
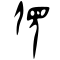 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Characters in the same phonetic series (父) (Zhengzhang, 2003) | |
|---|---|
| Old Chinese | |
| 抪 | *paː, *paːs |
| 布 | *paːs |
| 佈 | *paːs |
| 怖 | *pʰaːs |
| 斧 | *paʔ |
| 父 | *paʔ, *baʔ |
| 蚥 | *paʔ, *baʔ |
| 滏 | *baʔ |
| 釜 | *baʔ |
Pictogram (象形) – A hand holding a stone, referring to a man working with a stone axe.
Etymology
Old and Middle Chinese word for “father”: 父 (OC *paʔ, *baʔ).
Regular development from Middle Chinese would lead to the labiodental fù in Mandarin, but the colloquial word resisted the sound changes and is now written as 爸 (bà), with the 巴 (bā) phonetic component added to it to indicate the unchanged bilabial initial.
Pronunciation
- Mandarin
- Cantonese (Jyutping): fu2, fu6
- Hakka (Sixian, PFS): fù
- Min Nan (POJ): hū / hú
- Wu (Wiktionary): vu (T3)
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄈㄨˋ
- Wade-Giles: fu4
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: fuh
- IPA (key): /fu⁵¹/
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Jyutping: fu2, fu6
- Yale: fú, fuh
- Cantonese Pinyin: fu2, fu6
- IPA (key): /fuː³⁵/, /fuː²²/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: fù
- Hakka Romanization System: fuˇ
- Hagfa Pinyim: fu2
- IPA: /fu¹¹/
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Min Nan
- Wu
- (Shanghainese)
- Wiktionary: vu (T3)
- IPA (key): /v̻v̩ʷ²³/
- (Shanghainese)
| Rime | ||
|---|---|---|
| Character | 父 | 父 |
| Reading # | 1/2 | 2/2 |
| Initial (聲) | 幫 (1) | 並 (3) |
| Final (韻) | 虞 (24) | 虞 (24) |
| Tone (調) | Rising (X) | Rising (X) |
| Openness (開合) | Closed | Closed |
| Division (等) | III | III |
| Fanqie | 方矩切 | 扶雨切 |
| Reconstructions | ||
| Zhengzhang Shangfang |
/pɨoX/ | /bɨoX/ |
| Pan Wuyun |
/pioX/ | /bioX/ |
| Shao Rongfen |
/pioX/ | /bioX/ |
| Edwin Pulleyblank |
/puə̆X/ | /buə̆X/ |
| Li Rong |
/pioX/ | /bioX/ |
| Wang Li |
/pĭuX/ | /bĭuX/ |
| Bernard Karlgren |
/pi̯uX/ | /bʱi̯uX/ |
| Expected Mandarin Reflex |
fǔ | fù |
| Baxter-Sagart system 1.1 (2014) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Character | 父 | 父 |
| Reading # | 1/2 | 2/2 |
| Modern Beijing (Pinyin) |
fǔ | fù |
| Middle Chinese |
‹ pjuX › | ‹ bjuX › |
| Old Chinese |
/*p(r)aʔ/ | /*[N-p](r)aʔ/ |
| English | (respectful suffix in male names) | father |
Notes for Old Chinese notations in the Baxter-Sagart system: * Parentheses "()" indicate uncertain presence; | ||
| Zhengzhang system (2003) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Character | 父 | 父 |
| Reading # | 1/2 | 2/2 |
| No. | 3500 | 3504 |
| Phonetic component |
父 | 父 |
| Rime group |
魚 | 魚 |
| Rime subdivision |
0 | 0 |
| Corresponding MC rime |
甫 | 父 |
| Old Chinese |
/*paʔ/ | /*baʔ/ |
Definitions
父
Compounds
|
Japanese
Kanji
Readings
- Goon: ぶ (bu) (non-Jōyō reading), ふ (fu)
- Kan’on: ふ (fu)
- Kan’yōon: ほ (ho) (non-Jōyō reading)
- Kun: ちち (chichi)
Compounds
Derived terms
Antonyms
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 父 |
|
ちち Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
Pronunciation
- Kun'yomi
-
(Tokyo) ちち [ch
ìchíꜜ] (Odaka - [2])[1][2] -
(Tokyo) ちち [ch
íꜜchì] (Atamadaka - [1])[1][2] - IPA(key): [t͡ɕi̥t͡ɕi]
Noun
父 (hiragana ちち, romaji chichi)
- father
- c. 759, Man'yōshū (book 20, poem 4402)
- 知波夜布留 賀美乃美佐賀尓 奴佐麻都里 伊波布伊能知波 意毛知々我多米
- 931–938, Wamyō Ruijushō, book 1, page 115:
- 父爲考、和名知々、日本紀私記云加曾
- c. 759, Man'yōshū (book 20, poem 4402)
Etymology 2
From chichi. Eastern dialect.
Noun
父 (hiragana しし, romaji shishi)
- father
Etymology 3
From chichi.
Noun
- father
- 1603–1604, Nippo Jisho (page 649)
- Tete. l, chichi. テテ. まはは, チチ (てて. または, 父) 父親.
- 1603–1604, Nippo Jisho (page 649)
Etymology 4
From chichi.
Noun
- a childish term for one's father; daddy
- 1603–1604, Nippo Jisho (page 670)
- Toto. トト (とと) 父. これは子どもの使う語である.
- 1603–1604, Nippo Jisho (page 670)
Etymology 5
/kaso2/: *[kasə] > [kaso].
Noun
- father
- 931–938, Wamyō Ruijushō, book 1, page 115:
- 父爲考、和名知々、日本紀私記云加曾
- 931–938, Wamyō Ruijushō, book 1, page 115:
Etymology 6
From kaso. Medial -s- voices to /kazo/.
Noun
- father
References
- 1 2 2006, 大辞林 (Daijirin), Third Edition (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Sanseidō, ISBN 4-385-13905-9
- 1 2 1998, NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 (NHK Japanese Pronunciation Accent Dictionary) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: NHK, ISBN 978-4-14-011112-3
- Doi, Tadao (1603–1604) Hōyaku Nippo Jisho (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Iwanami Shoten, ISBN 978-4-00-080021-1, published 1980.
- Minamoto, Shitagō; Kyōto Daigaku Bungakubu Kokugogaku Kokubungaku Kenkyūshitu (931–938) Shohon Shūsei Wamyō Ruijushō: Honbunhen (in Japanese), Kyōto: Rinsen, ISBN 978-4-653-00507-0, published 1968.
- Satake, Akihiro; Hideo Yamada; Rikio Kudō; Masao Ōtani; Yoshiyuki Yamazaki (c. 759) Shin Nihon Koten Bungaku Taikei 4: Man’yōshū 4 (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Iwanami Shoten, ISBN 978-4-00-240004-4, published 2003.
Korean
Hanja
父 • (bu, bo)
Eumhun:
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.