Definify.com
Definition 2026
後
後
Translingual
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| | |||
Han character
後 (radical 60 彳+6, 9 strokes, cangjie input 竹人女戈水 (HOVIE), four-corner 22247, composition ⿰彳⿱幺夊)
References
- KangXi: page 366, character 18
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 10098
- Dae Jaweon: page 688, character 1
- Hanyu Da Zidian: volume 2, page 822, character 3
- Unihan data for U+5F8C
Chinese
| trad. | 後 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. | 后 | |
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 後
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Large seal script | Small seal script |
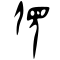 |
 |
 |
 |
Ideogrammic compound (會意) : 彳 + 幺 + 又.
Note that the simplified form 后 (OC *ɡoːʔ, *ɡoːs) is also a traditional character on its own, with a different meaning.
Pronunciation
- Mandarin
- Cantonese (Jyutping): hau6
- Hakka (Sixian, PFS): heu
- Min Dong (BUC): âu / hâiu / hâu
- Min Nan (POJ): āu / hō͘
- Wu (Wiktionary): hheu (T3)
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄏㄡˋ
- Wade-Giles: hou4
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: how
- IPA (key): /xoʊ̯⁵¹/
-

- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Jyutping: hau6
- Yale: hauh
- Cantonese Pinyin: hau6
- IPA (key): /hɐu̯²²/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: heu
- Hakka Romanization System: heu
- Hagfa Pinyim: heu4
- IPA: /he̯u⁵⁵/
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Min Dong
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: âu / hâiu / hâu
- IPA (key): /ɑu²⁴²/, /hɑu²⁴²/, /hɑu²⁴²/
- (Fuzhou)
- Min Nan
- (Hokkien)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: āu / hō͘
- Tâi-lô: āu / hōo
- Phofsit Daibuun: au, ho
- IPA (Xiamen): /aʊ²²/, /hɔ²²/
- IPA (Quanzhou): /aʊ⁴¹/, /hɔ⁴¹/
- IPA (Zhangzhou): /aʊ²²/, /hɔ²²/
- IPA (Taipei): /aʊ³³/, /hɔ³³/
- IPA (Kaohsiung): /aʊ³³/, /hɔ³³/
- (Hokkien)
- Wu
- (Shanghainese)
- Wiktionary: hheu (T3)
- IPA (key): /ɦɜ²³/
- (Shanghainese)
| Rime | ||
|---|---|---|
| Character | 後 | 後 |
| Reading # | 1/2 | 2/2 |
| Initial (聲) | 匣 (33) | 匣 (33) |
| Final (韻) | 侯 (137) | 侯 (137) |
| Tone (調) | Rising (X) | Departing (H) |
| Openness (開合) | Open | Open |
| Division (等) | I | I |
| Fanqie | 胡口切 | 胡遘切 |
| Reconstructions | ||
| Zhengzhang Shangfang |
/ɦəuX/ | /ɦəuH/ |
| Pan Wuyun |
/ɦəuX/ | /ɦəuH/ |
| Shao Rongfen |
/ɣəuX/ | /ɣəuH/ |
| Edwin Pulleyblank |
/ɦəwX/ | /ɦəwH/ |
| Li Rong |
/ɣuX/ | /ɣuH/ |
| Wang Li |
/ɣəuX/ | /ɣəuH/ |
| Bernard Karlgren |
/ɣə̯uX/ | /ɣə̯uH/ |
| Expected Mandarin Reflex |
hòu | hòu |
| Baxter-Sagart system 1.1 (2014) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Character | 後 | 後 |
| Reading # | 1/2 | 2/2 |
| Modern Beijing (Pinyin) |
hòu | hòu |
| Middle Chinese |
‹ huwX › | ‹ huwH › |
| Old Chinese |
/*[ɢ]ˤ(r)oʔ/ | /*[ɢ]ˤ(r)oʔ-s/ |
| English | after | put after ? |
Notes for Old Chinese notations in the Baxter-Sagart system: * Parentheses "()" indicate uncertain presence; | ||
| Zhengzhang system (2003) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Character | 後 | 後 |
| Reading # | 1/2 | 2/2 |
| No. | 5178 | 5179 |
| Phonetic component |
後 | 後 |
| Rime group |
侯 | 侯 |
| Rime subdivision |
0 | 0 |
| Corresponding MC rime |
厚 | 𠋫 |
| Old Chinese |
/*ɢoːʔ/ | /*ɢoːs/ |
| Notes | 甲文象足受系而遲後(文源) | |
Definitions
後
- behind; rear; back
- Antonyms: 前 (qián)
- later; after; afterwards
- descendants; offsprings
- anus
Compounds
|
|
|
Japanese
Kanji
Readings
- Goon: ぐ (gu) (non-Jōyō reading)
- Kan’on: こう (kō)
- Tōon: ご (go)
- Kun: あと (ato), うしろ (後, 後ろ, ushiro), おくれ (後, 後れ, okure), おくれる (後れる, okureru), しり (shiri), しりえ (後, 後方, shirie), のち (nochi), ゆり (yuri)
- Nanori: こし (koshi), し (shi), しい (shī)
Compounds
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 後 |
|
あと Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
Originally an extension of 跡 (ato, “footprint; leftover”), itself a compound of 足 (ato, “foot”) + 所 (to, “place”).[1][2][3]
Pronunciation
Noun
- (spatially) the back, the rear, behind
- (temporally) later, afterwards, some time after the present
- the rest
Etymology 2
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 後 |
|
うしろ Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
Probably from Old Japanese. Usage examples appear in texts from at least the 900s.[1] Ultimate derivation unknown.
Pronunciation
Alternative forms
- 後ろ (more common)
Noun
後 (hiragana うしろ, romaji ushiro)
Etymology 3
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 後 |
|
おくれ Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
The 連用形 (ren'yōkei, “continuative or stem form”) of verb 遅れる (okureru, “to be late; to be delayed; to come after something else”). Examples appear from at least the 1300s.[1]
Pronunciation
Alternative forms
Noun
後 (hiragana おくれ, romaji okure)
- something later, after, or behind
- inferiority
- uncertainty, nervousness, indecision
Etymology 4
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 後 |
|
しり Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
From Old Japanese. Ultimate derivation unknown.
Pronunciation
Alternative forms
- 尻 (much more common)
Noun
後 (hiragana しり, romaji shiri)
Etymology 5
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 後 |
|
しりえ Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
From Old Japanese. Compound of 尻 (shiri, “butt, tail, rear”) + 方 (e, “side, facing, way, direction”).
Pronunciation
- Kun'yomi
- (Tokyo) しりえ [shìríéꜜ] (Odaka - [3])[2]
- (Tokyo) しりえ [shìríé] (Heiban - [0])[2][4]
- IPA(key): [ɕiɾie̞]
Alternative forms
Noun
後 (hiragana しりえ, romaji shirie)
- the rear, back, or backside of something
- the rearward or backward direction
- the portion of a palace where a queen or other female imperial consort lives
Etymology 6
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 後 |
|
のち Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
From Old Japanese. Ultimate derivation unknown.
Pronunciation
- (Tokyo) のち [nòchíꜜ] (Odaka - [2])[2][4]
- (Tokyo) のち [nòchí] (Heiban - [0])[2][4]
- IPA(key): [no̞t͡ɕi]
Noun
後 (hiragana のち, romaji nochi)
- later, afterwards, some time after the present
Etymology 7
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 後 |
|
ゆり Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
From Old Japanese. Ultimate derivation unknown. May be cognate with より (yori, “from; after”).
Pronunciation
Noun
- (obsolete) later, afterwards, some time after the present
Etymology 8
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 後 |
|
ご Grade: 2 |
| on'yomi |
From Middle Chinese 後 (/ɦəuX/, /ɦəuH/, “after”). Classified as the tōon or "Tang sound", so likely borrowed from the dialects spoken during the Tang dynasty.
Pronunciation
Noun
- later, afterwards, some time after the present
Suffix
Etymology 9
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 後 |
|
こう Grade: 2 |
| on'yomi |
From Middle Chinese 後 (/ɦəuX/, “after”). Classified as the kan'on, so likely a later borrowing. Compare modern Mandarin reading hòu.
Pronunciation
Prefix
後 (hiragana こう, romaji kō-)
Usage notes
Only used in compounds. Never used in isolation.
References
- 1 2 3 1988, 国語大辞典(新装版) (Kokugo Dai Jiten, Revised Edition) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2006, 大辞林 (Daijirin), Third Edition (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Sanseidō, ISBN 4-385-13905-9
- ↑ 1995, 大辞泉 (Daijisen) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan, ISBN 4-09-501211-0
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1997, 新明解国語辞典 (Shin Meikai Kokugo Jiten), Fifth Edition (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Sanseidō, ISBN 4-385-13143-0
Korean
Hanja
後 • (hu) (hangeul 후, McCune-Reischauer hu, Yale hwu)
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.
Vietnamese
Han character
後 (hậu)
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.