Definify.com
Definition 2026
昔
昔
Translingual
Han character
昔 (radical 72 日+4, 8 strokes, cangjie input 廿日 (TA), four-corner 44601, composition ⿱龷日)
Derived characters
References
- KangXi: page 492, character 5
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 13816
- Dae Jaweon: page 855, character 2
- Hanyu Da Zidian: volume 2, page 1488, character 11
- Unihan data for U+6614
Chinese
|
simp. and trad. |
昔 | |
|---|---|---|
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 昔
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Bamboo and silk script | Large seal script | Small seal script |
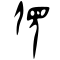 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Characters in the same phonetic series (昔) (Zhengzhang, 2003) | |
|---|---|
| Old Chinese | |
| 借 | *ʔsjaːɡs, *ʔsjaːɡ |
| 唶 | *ʔsjaːɡs |
| 藉 | *zjaːɡs, *zjaːɡ |
| 躤 | *zjaːɡs |
| 蜡 | *zraːɡs, *sʰaːɡs |
| 齰 | *zraːɡs, *zraːɡ |
| 醋 | *sʰaːɡs |
| 錯 | *sʰaːɡs, *sʰaːɡ |
| 措 | *sʰaːɡs |
| 厝 | *sʰaːɡs, *sʰaːɡ |
| 逪 | *sʰaːɡ |
| 剒 | *sʰaːɡ |
| 鵲 | *sʰaɡ |
| 碏 | *sʰaɡ |
| 踖 | *sʰaɡ, *ʔsjaːɡ, *zjaːɡ |
| 趞 | *sʰaɡ |
| 皵 | *sʰaɡ, *sʰjaːɡ |
| 舄 | *sʰjaːɡ, *sʰaɡ, *sjaːɡ, *sjaːɡ |
| 斮 | *ʔsraɡ, *ʔsraːɡ |
| 簎 | *zraːwɢ, *sʰraːɡ, *zjaːɡ |
| 諎 | *ʔsraːɡ |
| 矠 | *sʰreːɡ, *zreːɡ |
| 庴 | *ʔsjaːɡ, *zjaːɡ |
| 籍 | *zjaːɡ |
| 耤 | *zjaːɡ |
| 猎 | *zjaːɡ |
| 昔 | *sjaːɡ |
| 惜 | *sjaːɡ |
| 腊 | *sjaːɡ |
| 焟 | *sjaːɡ |
| 棤 | *sjaːɡ |
Oracle bone form: Ideogrammic compound (會意) : 𡿧 (“disaster; floods”) + 日 (“sun”) – the flood submerging the sun; the former times.
Shuowen: Two pieces of flesh (仌) left to dry in the sun (日). Original form of 腊 (OC *sjaːɡ).
Pronunciation 1
- Mandarin
- Cantonese (Jyutping): sik1
- Min Dong (BUC): sék
- Min Nan (POJ): siak / sek
- Wu (Wiktionary): xiq (T4)
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese, Mainland)+
- Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄒㄧ
- Wade-Giles: hsih1
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: shi
- IPA (key): /ɕi⁵⁵/
- (Standard Chinese, Taiwan)+
- Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄒㄧˊ
- Wade-Giles: hsih2
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: shyi
- IPA (key): /ɕi³⁵/
- (Standard Chinese, Mainland)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Jyutping: sik1
- Yale: sīk
- Cantonese Pinyin: sik7
- IPA (key): /sɪk̚⁵/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Min Dong
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: sék
- IPA (key): /sɛiʔ²⁴/
- (Fuzhou)
- Min Nan
- (Hokkien: Quanzhou)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: siak
- Tâi-lô: siak
- Phofsit Daibuun: siag
- IPA (Quanzhou): /ɕiak̚⁵/
- (Hokkien: mainstream Taiwanese, Xiamen, Zhangzhou)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: sek
- Tâi-lô: sik
- Phofsit Daibuun: seg
- IPA (Taipei): /ɕiɪk̚³²/
- IPA (Kaohsiung): /ɕiɪk̚³²/
- IPA (Xiamen): /ɕiɪk̚³²/
- IPA (Zhangzhou): /ɕiɪk̚³²/
- (Hokkien: Quanzhou)
- Wu
- (Shanghainese)
- Wiktionary: xiq (T4)
- IPA (key): /ɕi̯ɪʔ⁵⁵/
- (Shanghainese)
| Rime | |
|---|---|
| Character | 昔 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| Initial (聲) | 心 (16) |
| Final (韻) | 昔 (123) |
| Tone (調) | Checked (Ø) |
| Openness (開合) | Open |
| Division (等) | III |
| Fanqie | 思積切 |
| Reconstructions | |
| Zhengzhang Shangfang |
/siᴇk̚/ |
| Pan Wuyun |
/siɛk̚/ |
| Shao Rongfen |
/siæk̚/ |
| Edwin Pulleyblank |
/siajk̚/ |
| Li Rong |
/siɛk̚/ |
| Wang Li |
/sĭɛk̚/ |
| Bernard Karlgren |
/si̯ɛk̚/ |
| Expected Mandarin Reflex |
xi |
| Baxter-Sagart system 1.1 (2014) | |
|---|---|
| Character | 昔 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| Modern Beijing (Pinyin) |
xī |
| Middle Chinese |
‹ sjek › |
| Old Chinese |
/*[s]Ak/ |
| English | in the past |
Notes for Old Chinese notations in the Baxter-Sagart system: * Parentheses "()" indicate uncertain presence; | |
| Zhengzhang system (2003) | |
|---|---|
| Character | 昔 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| No. | 13309 |
| Phonetic component |
昔 |
| Rime group |
鐸 |
| Rime subdivision |
0 |
| Corresponding MC rime |
昔 |
| Old Chinese |
/*sjaːɡ/ |
Definitions
昔
- †dried meat
- former times; the past
- †yesterday
- †sunset; dusk
- †Alternative form of 夕 (xī, “evening; night”).
- A surname.
Compounds
Pronunciation 2
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄘㄨㄛˋ
- Wade-Giles: ts'o4
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: tsuoh
- IPA (key): /t͡sʰu̯ɔ⁵¹/
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
Definitions
昔
- †coarse; rough
- †Alternative form of 錯/错 (cuò, “to criss-cross”).
- †Alternative form of 措 (cuò, “to use; to carry out”).
Japanese
Kanji
Readings
Etymology
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 昔 |
|
むかし Grade: 3 |
| kun'yomi |
From Old Japanese. The muka portion derives from the 未然形 (mizenkei, “incomplete form”) of verb 向く (muku, “to face opposite to something”), implying “that which stands opposite from the present”. The shi portion is suffix し (shi) indicating direction, also found in words 縦し (tatashi, “the standing or vertical direction”), 横し (yokoshi, “the sideways or horizontal direction”). This appears to be a somewhat rare alternative form, more commonly encountered as さ (sa), and may be cognate with the nominalizing adjective ending さ (sa).[1]
Pronunciation
Adverb
昔 (hiragana むかし, romaji mukashi)
- once (in the indeterminate past)
- 昔見た映画
- mukashi mita eiga
- a movie I once saw
- 昔見た映画
Noun
昔 (hiragana むかし, romaji mukashi)
- the past, old times
- 970-999, Utsubo Monogatari (Toshikage)[3]
- むかし、式部大輔、左大弁かけて清原の王ありけり。
- 970-999, Utsubo Monogatari (Toshikage)[3]
- ancient
- 昔の人 — ancient people
- もう昔の話だ。— That's ancient history.
References
- ↑ 1988, 国語大辞典(新装版) (Kokugo Dai Jiten, Revised Edition) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan
- ↑ 2006, 大辞林 (Daijirin), Third Edition (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Sanseidō, ISBN 4-385-13905-9
- ↑ Kōno, Tama (c. 970–999) Nihon Koten Bungaku Taikei 10: Utsubo Monogatari 1 (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Iwanami Shoten, ISBN 978-4-00-060010-1, published 1959.
Korean
Hanja
昔 • (seok, chak) (hangeul 석, 착, revised seok, chak, McCune-Reischauer sŏk, ch'ak, Yale sek, chak)
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.