Definify.com
Definition 2026
이
이
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Korean
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /i/
- Phonetic hangeul: 이
| Revised transcription | i |
| Revised transliteration | i |
| McCune–Reischauer | i |
| Yale | i |
Etymology 1
|
이익읶읷인읹읺 읻일읽읾읿잀잁 잂잃임입잆잇있 잉잊잋잌잍잎잏 | |
| 의 ← | → 자 |
|---|---|
Syllable
이 • (i)
Etymology 2
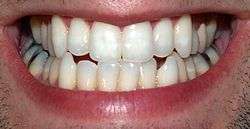
First attested in the Seokbo sangjeol (釋譜詳節 / 석보상절), 1447, as 니 (Yale: ni).
Noun
이 • (i)
Alternative forms
- 니 (ni) (archaic, now suffixal)
Synonyms
- 이빨 (ippal)
- 치아 (chia)
Derived terms
- 덧니 (deonni, “snaggletooth/teeth”)
- 송곳니 (songgonni, “canine tooth/teeth”)
- 아랫니 (araenni, “lower tooth/teeth”)
- 앞니 (amni, “incisor(s)”)
- 윗니 (winni, “upper tooth/teeth”)
- 어금니 (eogeumni, “molar(s)”)
Etymology 3
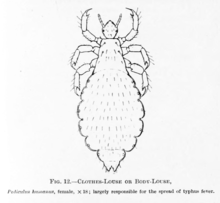
First attested in the Hunmong jahoe (訓蒙字會 / 훈몽자회), 1527, as 니 (Yale: ni).
Noun
이 • (i)
Derived terms
- 거웃니 (geounni, “pubic louse”)
- 닭니 (dangni, “bird louse”)
- 머릿니 (meorinni, “head louse”)
- 사면발니 (samyeonballi, “crab louse”)
- 옷엣니 (osenni, “body louse”)
Etymology 4
First attested in the Hunmin jeongeum eonhae (訓民正音諺解本 / 훈민정음언해본), 1447, as 이 (Yale: i).
Determiner
이 • (i)
- this
- 이 그림을 본 적이 있다. (i geurimeul bon jeogi itda.) I have seen this picture.
Pronoun
이 • (i)
See also
| Korean demonstratives edit | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Determiner | 이 | 그 | 저 | 어느 | |
| Pronoun | Human | 이이 | 그이 | 저이 | |
| 이분 | 그분 | 저분 | |||
| 이자 | 그자 | 저자 | |||
| 이놈 | 그놈 | 저놈 | |||
| 이년 | 그년 | 저년 | |||
| 얘 | 걔 | 쟤 | |||
| Object | 이 | (그) | (저) | ||
| 이것 | 그것 | 저것 | 어느 것 | ||
| 이거 | 그거 | 저거 | 어느 거 | ||
| Place | 여기 | 거기 | 저기 | 어디 | |
| 이곳 | 그곳 | 저곳 | |||
| Direction | 이쪽 | 그쪽 | 저쪽 | 어느 쪽 | |
| Time | 이때 | 그때 | 접때 | ||
| Verb | 이러다 | 그러다 | 저러다 | 어쩌다 | |
| Adjective | 이렇다 | 그렇다 | 저렇다 | 어떻다 | |
| 이러하다 | 그러하다 | 저러하다 | 어떠하다 | ||
| Adverb | 이리 | 그리 | 저리 | 어찌 | |
| 이렇게 | 그렇게 | 저렇게 | 어떻게 | ||
| 이만큼 | 그만큼 | 저만큼 | |||
Etymology 5
Of native Korean origin. Possibly cognate with Old Japanese い (i, emphatic nominative particle).
Particle
이 • (i)
- A particle marking a grammatical subject ending with a consonant.
- A particle marking a grammatical complement ending with a consonant, before 되다 (doeda, “to become”) and 아니다 (anida, “(to be) not”).
이 • (i)
- A semantic particle which adheres to and puts emphasis on a noun or an adverb.
Synonyms
- 가 (ga) (marks a grammatical subject ending with a vowel)
See also
- 은 (eun) (marks a topic word or phrase ending with a consonant)
- 는 (neun) (marks a topic word or phrase ending with a vowel)
- 을 (eul) (marks a direct object ending with a consonant)
- 를 (reul) (marks a direct object ending with a vowel)
- Old Japanese い (i); emphatic nominative marker
Etymology 6
Of native Korean origin.
Suffix
이 • (i)
- a suffix deriving a passive verb.
이 • (i)
- a suffix deriving a causative verb.
- 저는 희망을 봅니다. (Jeoneun huimang-eul bomnida., “I see hope.”) → 저는 이분들께 희망을 보여 드리고 싶습니다. (Jeoneun ibundeulkke huimang-eul boyeo deurigo sipseumnida., “I want to show these people hope.”)
- 천장이 높군. (Cheonjang-i nopgun., “The ceiling is high.”) → 천장을 높이어야(하)겠군. (Cheonjang-eul nopieoya(ha)getgun., “I guess the ceiling needs raising.”)
Synonyms
- -히 (hi)/리 (ri)/기 (gi)- : suffixes deriving passive verbs.
- -히 (hi)/리 (ri)/기 (gi)/우 (u)/구 (gu)/는 (neun)- : suffixes deriving causative verbs.
Etymology 7
First attested in the Yongbi eocheonga (龍飛御天歌 / 용비어천가), 1447, as 이 (Yale: i).
Noun
이 • (i)
- (dependent) a person.
Etymology 8
Of native Korean origin.
Suffix
이 • (i)
- (after a stem of a verb or an adjective) a suffix deriving a noun.
- (in the form of a noun + a stem of a verb + suffix 이) a suffix deriving a noun, adding a meaning of a person, an item, or an event. -er.
- a suffix deriving a noun, adding a meaning of a person or an item. -er.
Etymology 9
Of native Korean origin.
Suffix
이 • (i)
- (after a stem of an adjective) a suffix deriving an adverb. -ly.
- (after repeating a single-syllable noun) a suffix deriving an adverb.
Usage notes
The suffix -i is used for adjectives not ending in -hada, and the suffix -hi is implemented for that case. For example, 많다 (manta, “many”) turns into 많이 (mani, “a lot”) whereas 깔끔하다 (kkalkkeumhada, “neat”) becomes 깔끔히 (kkalkkeumhi, “neatly”). However, if -hada is suffixed after consonants k and s, -i is sometimes used rather than -hi, as in 깊숙이 (gipsugi, “deeply”) from 깊숙하다 (gipsukhada, “deep”) and 깨끗이 (kkaekkeusi, “cleanly”) from 깨끗하다 (kkaekkeuthada, “clean”), while many adjectives like 솔직하다 (soljikhada, “frank”) still take -hi. Whether to use -i or -hi depends on its pronunciation, which is very confusing even to natives.[1]
The conjugation for this suffix is similar to the infinite form, but not the same. Especially, the p-irregular adjectives (ㅂ 불규칙 용언) take 이 (i) not 위 (wi); for instance, 가깝다 (gakkapda, “near”) → 가까이 (gakkai, “nearly”).
Also, note that only a limited number of adverbs are frequently used which are formed by affixing -i or -hi.
See also
- -히 (hi)
Etymology 10
Of native Korean origin.
Suffix
이 • (i)
- (after the stem of the sequential form of an adjective) one of the familiar style declarative endings.
Etymology 11
Korean reading of various Chinese characters.
Alternative forms
- 리 (ri) (ri) (North Korean) (for many but not all characters)
Noun
이 • (i)
- 理 (philosophy) (cosmic) reason
Numeral
- (cardinal) two
Usage notes
- Used primarily with Sino-Korean count words, or in reading numbers literally. In Modern Korean, numbers are almost always written in Arabic numerals.
Proper noun
이 • (I) (hanja 李)
- The second most common Korean surname, South Korean spelling.
Usage notes
- Most commonly romanized as Lee. Other romanizations include Li, Yi, Ri, and Rhee. It is written as 리 (Ri) in North Korea.
Syllable
이 (i)
- 李: plum tree
- (eumhun reading: 오얏나무 이 (oyannamu i))
- 二: two
- (eumhun reading: 두 이 (du i))
- 理: ruling
- (eumhun reading: 다스릴 이 (daseuril i))
- 里: village
- (eumhun reading: 마을 이 (ma-eul i))
- 利: beneficial
- (eumhun reading: 이로울 이 (iroul i))
- 以: 써
- 異: other
- (eumhun reading: 다를 이 (dareul i))
- 移: moving
- (eumhun reading: 옮길 이 (omgil i))
- 伊: that
- (eumhun reading: 저 이 (jeo i))
- 離: leaving
- (eumhun reading: 떠날 이 (tteonal i))
- 耳: ear
- (eumhun reading: 귀 이 (gwi i))
- 梨: pear tree
- (eumhun reading: 배나무 이 (baenamu i))
- 吏: petty official
- (eumhun reading: 아전 이 (ajeon i))
- 而: continuing speech
- (eumhun reading: 말이을 이 (marieul i))
- 易: easy
- (eumhun reading: 쉬울 이 (swiul i))
- 已: already
- (eumhun reading: 이미 이 (imi i))
- 夷: barbarian
- (eumhun reading: 오랑캐 이 (orangkae i))
- 貳: two
- (eumhun reading: 두 이 (du i))
- 彛:
- 怡:
- 爾:
- 裏:
- 履:
- 裡:
- 痍:
- 珥:
- 痢:
- 餌:
- 姨:
- 飴:
- 珥:
- 罹:
- 肄:
- 裡:
- 荑:
- 貽:
- 邇:
Synonyms
(two): 둘 (dul) (native Korean)